Publications
Publications are listed in reverse chronological order.
* denotes equal contribution.
2023
-
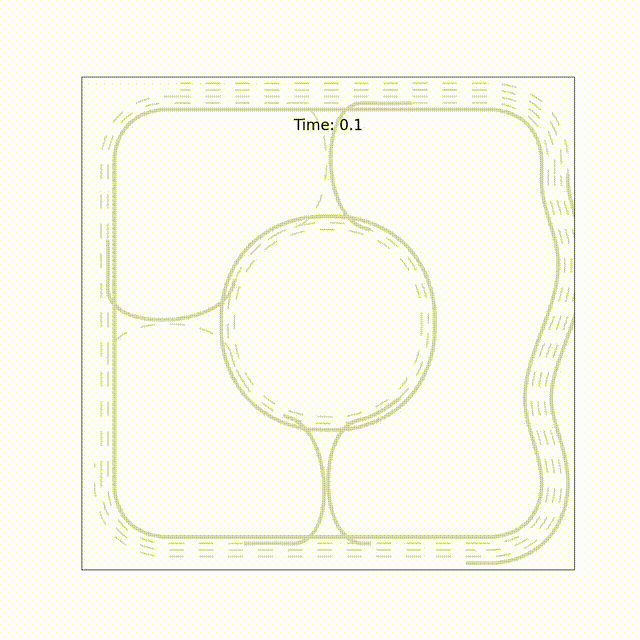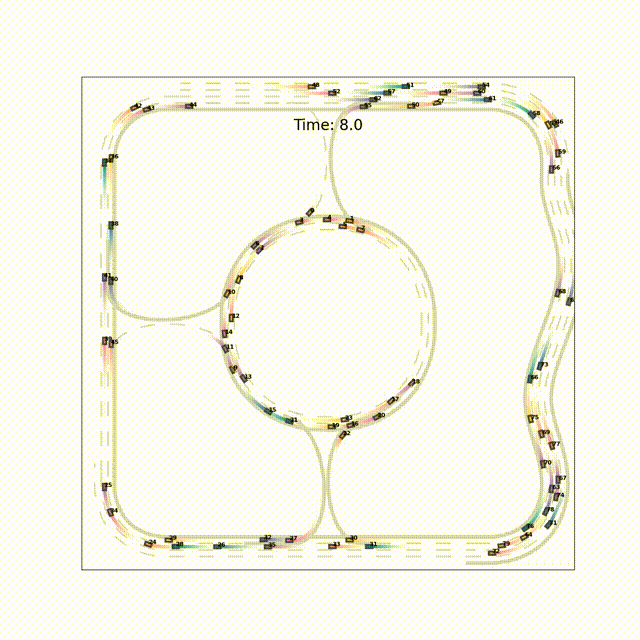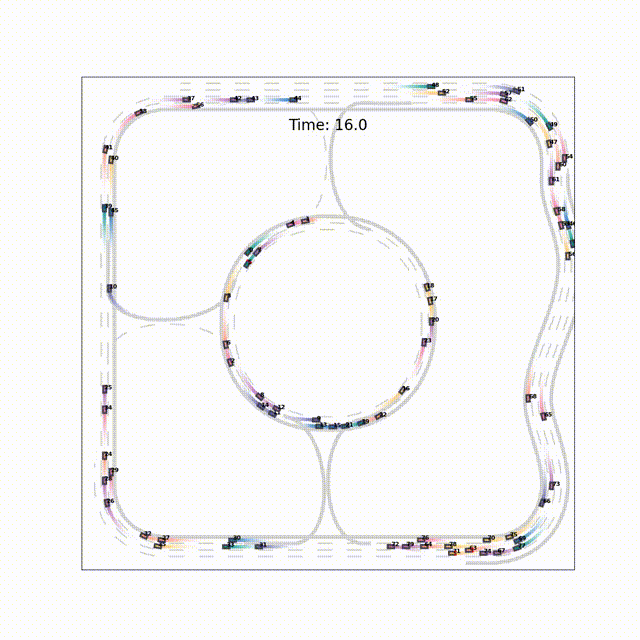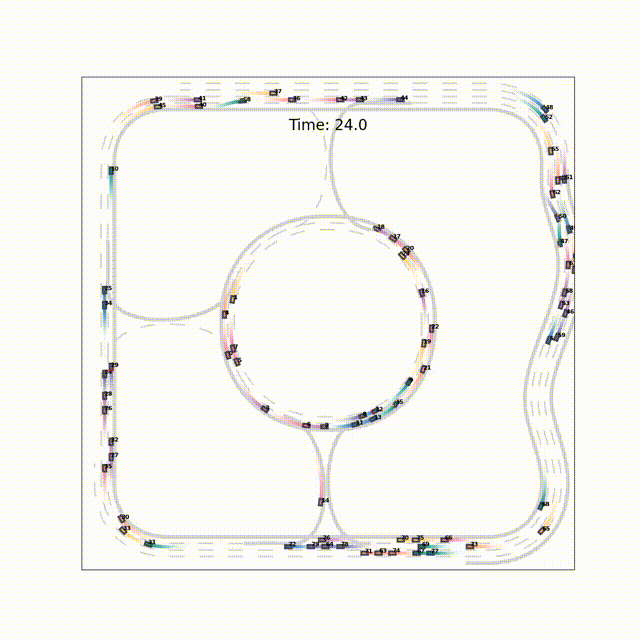 TrafficMCTS: A Closed-Loop Traffic Flow Generation Framework with Group-Based Monte Carlo Tree SearchZe Fu*, Licheng Wen*, Pinlong Cai, and 3 more authors2023
TrafficMCTS: A Closed-Loop Traffic Flow Generation Framework with Group-Based Monte Carlo Tree SearchZe Fu*, Licheng Wen*, Pinlong Cai, and 3 more authors2023Digital twins for intelligent transportation systems are currently attracting great interests, in which generating realistic, diverse, and human-like traffic flow in simulations is a formidable challenge. Current approaches often hinge on predefined driver models, objective optimization, or reliance on pre-recorded driving datasets, imposing limitations on their scalability, versatility, and adaptability. In this paper, we introduce TrafficMCTS, an innovative framework that harnesses the synergy of groupbased Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) and Social Value Orientation (SVO) to engender a multifaceted traffic flow replete with varying driving styles and cooperative tendencies. Anchored by a closed-loop architecture, our framework enables vehicles to dynamically adapt to their environment in real time, and ensure feasible collision-free trajectories. Through comprehensive comparisons with state-of-the-art methods, we illuminate the advantages of our approach in terms of computational efficiency, planning success rate, intent completion time, and diversity metrics. Besides, we simulate highway and roundabout scenarios to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework and highlight its ability to induce diverse social behaviors within the traffic flow. Finally, we validate the scalability of TrafficMCTS by showcasing its prowess in simultaneously mass vehicles within a sprawling road network, cultivating a landscape of traffic flow that mirrors the intricacies of human behavior.
@misc{wen2023trafficmcts, title = {TrafficMCTS: A Closed-Loop Traffic Flow Generation Framework with Group-Based Monte Carlo Tree Search}, author = {Fu*, Ze and Wen*, Licheng and Cai, Pinlong and Fu, Daocheng and Mao, Song and Shi, Botian}, year = {2023}, primaryclass = {cs.RO}, video = {https://youtu.be/Tr0QWCasO54} } - PreprintSwing Leg Motion Strategy for Heavy-load Legged Robot Based on Force SensingZe Fu, Yinghui Li, and Weizhong Guo2023
The heavy-load legged robot has strong load carrying capacity and can adapt to various unstructured terrains. But the large weight results in higher requirements for motion stability and environmental perception ability. In order to utilize force sensing information to improve its motion performance, in this paper, we propose a finite state machine model for the swing leg in the static gait by imitating the movement of the elephant. Based on the presence or absence of additional terrain information, different trajectory planning strategies are provided for the swing leg to enhance the success rate of stepping and save energy. The experimental results on a novel quadruped robot show that our method has strong robustness and can enable heavy-load legged robots to pass through various complex terrains autonomously and smoothly.
@misc{fu2023swing, title = {Swing Leg Motion Strategy for Heavy-load Legged Robot Based on Force Sensing}, author = {Fu, Ze and Li, Yinghui and Guo, Weizhong}, year = {2023}, primaryclass = {cs.RO}, } -
 Design of a Novel Wheel-Legged Robot with Rim Shape Changeable WheelsZe Fu, Hao Xu, Yinghui Li, and 1 more authorIn Advances in Mechanism, Machine Science and Engineering in China, 2023
Design of a Novel Wheel-Legged Robot with Rim Shape Changeable WheelsZe Fu, Hao Xu, Yinghui Li, and 1 more authorIn Advances in Mechanism, Machine Science and Engineering in China, 2023The wheel-legged hybrid structure has been utilized by ground mobile platforms in recent years to achieve good mobility on both flat surface and rough terrain. However, many designs of the obstacle-crossing part and transformation driving part of this structure is highly coupled, which limits its optimal performance in both aspects. This paper presents a novel wheel-legged robot with rim shape changeable wheels, which has the bi-directional and smooth obstacle-crossing ability. Based on the kinematic model, the geometric parameters of the wheel structure and the design variables of the driving four-bar mechanism are optimized separately. Experiments show that the prototype installed with the novel transformable wheel can overcome steps with the height of 1.52 times of its wheel radius with less fluctuation of its centroid and performs good locomotion capabilities in different environments.
@inproceedings{10.1007/978-981-19-9398-5_17, author = {Fu, Ze and Xu, Hao and Li, Yinghui and Guo, Weizhong}, editor = {Liu, Xinjun}, title = {Design of a Novel Wheel-Legged Robot with Rim Shape Changeable Wheels}, booktitle = {Advances in Mechanism, Machine Science and Engineering in China}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Springer Nature Singapore}, address = {Singapore}, pages = {315--328}, isbn = {978-981-19-9398-5}, }
2022
- CJMEDesign of A Novel Wheel-legged Robot with Rim Shape Changeable WheelsZe Fu, Hao Xu, Yinghui Li, and 1 more author2022
The wheel-legged hybrid structure has been utilized by ground mobile platforms in recent years to achieve good mobility on both flat surface and rough terrain. However, most of the wheel-legged robots only have one-directional obstacle-crossing ability. And during the motion, most of the wheel-legged robots’ centroid fluctuates violently, which damages the stability of the load. What’s more, many designs of the obstacle-crossing part and transformation driving part of this structure is highly coupled, which limits its optimal performance in both aspects. This paper presents a novel wheel-legged robot with rim shape changeable wheel, which has the bi-directional and smooth obstacle-crossing ability. Based on the kinematic model, the geometric parameters of the wheel structure and the design variables of the driving four-bar mechanism are optimized separately. The kinetostatics model of the mobile platform when climbing stairs is established to determine the body length and angular velocity of the driving wheels. A prototype is made according to the optimal parameters. Experiments show that the prototype installed with the novel transformable wheels can overcome steps with the height of 1.52 times of its wheel radius with less fluctuation of its centroid and performs good locomotion capabilities in different environments.
@misc{PPR:PPR559767, title = {Design of A Novel Wheel-legged Robot with Rim Shape Changeable Wheels}, author = {Fu, Ze and Xu, Hao and Li, Yinghui and Guo, Weizhong}, doi = {10.21203/rs.3.rs-2100682/v1}, publisher = {Research Square}, year = {2022}, }